The Capital Budgeting Decision , Macmillan, 8 th edition. Managerial Economics , Prentice-Hall. By rebalancing, you’ll ensure that your portfolio does not overemphasize one or more asset categories, and you’ll return your portfolio to a comfortable level of risk. Thus investment decisions are commitment of money resources at different time in expectation of economic returns in future dates.
Strategic financial management [1] is the study of finance with a long term view considering the strategic goals of the enterprise. Financial management is nowadays increasingly referred financial assets investment decision as «Strategic Financial Management» so as to give it an increased frame of reference. To financial assets investment decision what strategic financial management is about, we must first understand what is meant by the term «Strategic». Which is something that is done as part of a plan that is meant to achieve a particular purpose. Therefore, Strategic Financial Management are those aspect of the overall plan of the organisation that concerns financial managers. This includes different parts of the business plan, for example marketing and sales plan, production plan, personnel plan, capital expenditure.

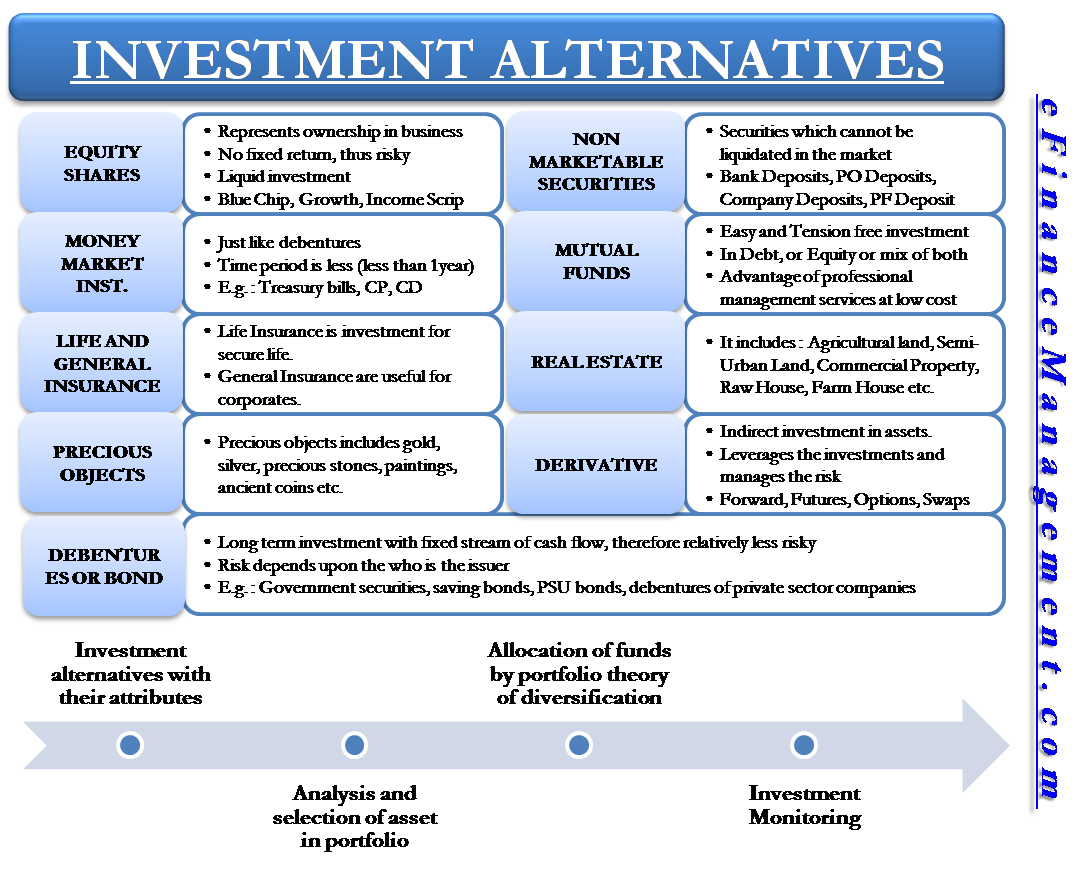
A financial asset is a liquid asset that gets its value from a contractual right or ownership claim. Cash, stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and bank deposits are all are examples of financial assets. Unlike land, property, commodities, or other tangible physical assets, financial assets do not necessarily have inherent physical worth or even a physical form. Rather, their value reflects factors of supply and demand in the marketplace in which they trade, as well as the degree of risk they carry. Most assets are categorized as either real, financial, or intangible. Real assets are physical assets that draw their value from substances or properties, such as precious metals, land, real estate, and commodities like soybeans, wheat, oil, and iron. Intangible assets are the valuable property that is not physical in nature.
A financial asset is a liquid asset that gets its value from a contractual right or ownership claim. Cash, stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and bank deposits are all are examples of financial assets. Unlike land, property, commodities, or other tangible physical assets, financial assets do not necessarily have inherent physical worth or even a physical form.
Rather, their value reflects factors of supply and demand in the marketplace in which they trade, as well as the degree of risk they carry. Most assets are categorized as either real, financial, or intangible. Real assets are physical assets that draw their value from substances or properties, such as precious metals, land, real estate, and commodities like soybeans, wheat, oil, and iron.
Intangible assets are the valuable property that is not physical in nature. They include patents, trademarks, and intellectual property. Financial assets are in-between the other two assets. Financial assets may seem intangible—non-physical—with only the stated value on a piece of paper such as a dollar bill or a listing on a computer screen. What that paper or listing represents, though, is a claim of ownership of an entity, like a public company, or contractual rights to payments—say, the interest income from a bond.
Financial assets derive their value from a contractual claim on an underlying asset. This underlying asset may be either real or intangible. REITs are financial assets and are publicly traded entities that own a portfolio of properties.
The Internal Revenue Service IRS requires businesses to report financial and real assets together as tangible assets for tax purposes. The grouping of tangible assets is separate from intangible assets.
The purest form of financial assets is cash and cash equivalents—checking accounts, savings accounts, and money market accounts. Liquid accounts are easily turned into funds for paying bills and covering financial emergencies or pressing demands.
Other varieties of financial assets might not be as liquid. Liquidity is the ability to change a financial asset into cash quickly. For stocks, it is the ability of an investor to buy or sell holdings from a ready market. Liquid markets are those where there are plenty of buyers and plenty of sellers and no extended lag-time in trying to execute a trade. In the case of equities like stocks and bonds, an investor has to sell and wait for the settlement date to receive their money—usually two business days.
Other financial assets have varying lengths of settlement. Maintaining funds in liquid financial assets can result in greater preservation of capital. Liquid assets like checking and savings accounts have a limited return on investment ROI capability. ROI is the profit you receive from an asset less than the cost of owning that asset.
In checking and savings accounts the ROI is minimal. They may provide modest interest income but, unlike equities, they offer little appreciation. Also, CDs financial assets investment decision money market accounts restrict withdrawals for months or years.
When interest rates fall, callable CDs are often called, and investors end up moving their money to potentially lower-income investments. The opposite of a liquid asset is an illiquid asset. Real estate and fine antiques are examples of illiquid financial assets. These items have value but cannot convert into cash quickly. Another example of an illiquid financial asset are stocks that do not have a high volume of trading on the markets.
Often these are investments like penny stocks or high-yield, speculative investments where there may not be a ready buyer when you are ready to sell. Keeping too much money tied up in illiquid investments has drawbacks—even in ordinary situations. Businesses, as well as individuals, hold financial assets. In the case of an investment or asset management company, the financial assets include the money in the portfolios firm handles for clients, called assets under management AUM.
For example, BlackRock Inc. In the case of banks, financial assets include the worth of the outstanding loans it has made to customers. Capital One, the 10th largest bank in the U. Fixed Income Essentials. Business Essentials. Investing Essentials. Money Market Account. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. What Is a Financial Asset? A financial asset’s worth may be based on an underlying tangible or real asset, but market supply and demand influence its value as.
Stocks, bonds, cash, CDs, and bank deposits are examples of financial assets. Aside from cash, the more common types of financial assets that investors encounter are:.
Stocks are financial assets with no set ending or expiration date. An investor buying stocks becomes part-owner of a company and shares in its profits and losses. Stocks may be held indefinitely or sold to other investors. Bonds are one way that companies or governments finance short-term projects.
The bondholder is the lender, and the bonds state how much money is owed, the interest rate being paid, and the bond’s maturity date.
A certificate of deposit CD allows an investor to deposit an amount of money at a bank for a specified period with a guaranteed interest rate. Pros Liquid financial assets convert into cash easily. Some financial assets have the ability to appreciate in value. Cons Highly liquid financial assets have little appreciation Illiquid financial assets may be hard to convert to cash.
The value of a financial asset is only as strong as the underlying entity. Compare Investment Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation.
Related Terms Real Asset, a Tangible Investment A real asset is a tangible investment, such as gold, real estate or oil, that has an intrinsic value due to its substance and physical properties. What Are Nonfinancial Assets? A nonfinancial asset is an asset with a physical value such as real estate, equipment, machinery, gold, or oil.
Near Money Definition Near money is a financial economics term financial assets investment decision non-cash assets that are highly liquid, such as savings accounts, CDs, and Treasury bills. Short-Term Investments Short-term investments are liquid assets designed to provide a safe harbor for cash while it awaits future deployment into higher-returning opportunities. Liquid Asset A liquid asset is an asset that can easily be converted into cash within a short amount of time.
In a Word: Liquidity Liquidity refers to the speed with which an asset or security can be bought or sold in the market, without affecting its price—the ease of converting it to ready money, or cash.
Cash is considered the most liquid of assets. Partner Links. Related Articles. Business Essentials Liquidity vs. Liquid Assets: What’s the Difference? Investing Essentials Are stocks real assets?
In other words, investment decisions are concerned with the question whether adding to capital assets today will increase the revenues of tomorrow to cover costs. Before you make any decision, consider these areas of importance:. Google Scholar. Journal of Business 45, Rubinstein, M. The cost of debt Cd is the contracted rate of financal payable on the borrowed capital after adjusting tax liability of the company.

Comments
Post a Comment