What Is Cumulative Interest? A lot of people have asked me to include a single formula for compound interest with monthly additions. Another method is to compare a loan’s interest rate to its annual percentage rate APR , which the TILA also requires lenders to disclose. The calculator, conversely, adds the deposit in first before calculating the interest.
Interactive compound interest formula
Compound interest or compounding interest is interest calculated on the initial principal, which also includes all of the accumulated interest of previous periods of a deposit or loan. The rate at which compound interest accrues depends on the frequency of compounding, such that the higher the number of compounding periods, the greater the compound. Since the interest-on-interest effect can generate increasingly positive returns based on the initial principal amount, it has sometimes been referred to as compound interest investment formula «miracle of compound. Compound interest is calculated by multiplying the initial principal amount by one plus the annual interest rate raised to the number of compound periods minus one. The total initial amount of the loan fromula then subtracted from investmeny resulting value. What would be the amount of interest? Using the above example, since compound interest also takes into consideration accumulated interest in previous periods, the interest amount is not the same for all three years, as it would be with simple .
Interactive compound interest formula

Compound interest is the addition of interest to the principal sum of a loan or deposit, or in other words, interest on interest. It is the result of reinvesting interest, rather than paying it out, so that interest in the next period is then earned on the principal sum plus previously accumulated interest. Compound interest is standard in finance and economics. Compound interest is contrasted with simple interest , where previously accumulated interest is not added to the principal amount of the current period, so there is no compounding. The simple annual interest rate is the interest amount per period, multiplied by the number of periods per year. The simple annual interest rate is also known as the nominal interest rate not to be confused with the interest rate not adjusted for inflation , which goes by the same name. The compounding frequency is the number of times per year or rarely, another unit of time the accumulated interest is paid out, or capitalized credited to the account , on a regular basis.
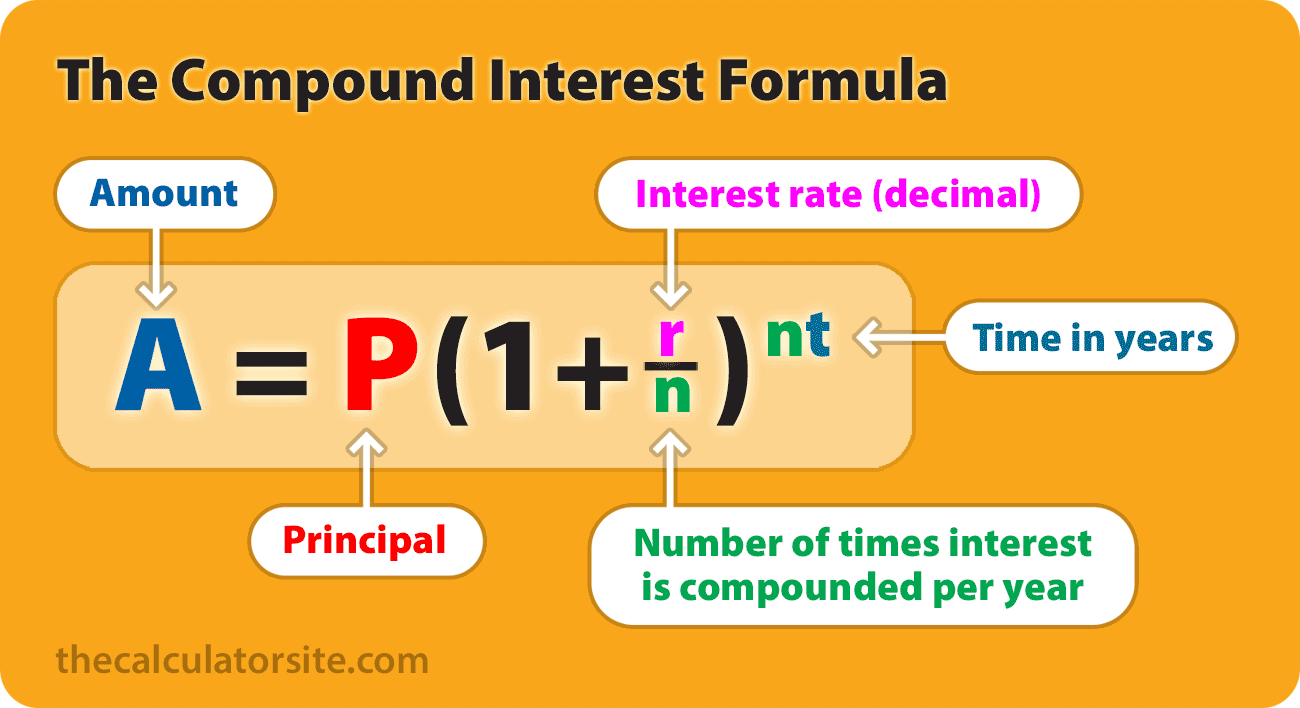
How to use the compound interest formula
Compound interest is the addition of interest to the principal sum of a loan or deposit, or in other words, interest on. It is the result of reinvesting interest, rather than paying it out, so that interest in the next period is then earned on the principal sum plus previously accumulated. Compound interest is standard in finance and economics. Compound interest is contrasted with simple interestwhere previously accumulated interest is not added to the principal amount of the current period, so there is no compounding.
The simple annual interest rate is the interest amount per period, multiplied by the number of periods per year. The simple annual interest rate is also known as the nominal interest rate not to be confused with the interest rate not adjusted for inflationwhich goes by the same. The compounding frequency is the number of times per year or rarely, another unit of time the accumulated interest is paid out, or capitalized credited to the accounton a regular basis.
The frequency could be yearly, half-yearly, quarterly, monthly, weekly, daily, or continuously or not at all, until maturity. For example, monthly capitalization with interest expressed as an annual rate means that the compounding frequency is 12, with time periods measured in months. The nominal rate cannot be directly compared between loans with different compounding frequencies.
Both the nominal interest rate and the compounding frequency are required in order to compare interest-bearing financial instruments. To help consumers compare retail financial products more fairly and easily, many countries require financial institutions to disclose the annual compound interest rate on deposits or advances on a comparable basis.
The interest rate on an annual equivalent basis may be referred to variously in different markets as annual percentage rate APRannual equivalent rate AEReffective interest rateeffective annual rateannual percentage yield and other terms. The effective annual rate is the total accumulated interest that would be payable up to the end of one year, divided by the principal sum.
The total compound interest generated is the final value minus the initial principal: [4]. This is very unusual in practice. The interest is less compared with the previous case, as a result of the lower compounding frequency.
Since the principal P is simply a coefficient, it is often dropped for simplicity, and the resulting accumulation function is used instead.
Accumulation functions for simple and compound interest are. Continuous compounding can be thought of as making the compounding period infinitesimally small, achieved by taking the limit as n goes to infinity. See definitions of the exponential function for the mathematical proof of this limit.
The amount after t periods of continuous compounding can be expressed in terms of the initial amount P 0 as. In mathematics, the accumulation functions are often expressed in terms of ethe base of the natural logarithm. This facilitates the use of calculus to manipulate interest formulae.
For any continuously differentiable accumulation function a tthe force of interest, or more generally the logarithmic or continuously compounded return is a function of time defined as follows:. This is the logarithmic derivative of the accumulation function. When the above formula is written in differential equation format, then the force of interest is simply the coefficient of amount of change:. For compound interest with a constant annual interest rate rthe force of interest is a constant, and the accumulation function of compounding interest in terms of force of interest is a simple power of e :.
The force of interest is less than the annual effective interest rate, but more than the annual effective discount rate. It is the reciprocal of the e -folding time. See also notation of interest rates. The interest on loans and mortgages that are amortized—that is, have a smooth monthly payment until the loan has been paid off—is often compounded monthly.
The formula for payments is found from the following argument. This can be derived by considering how much is left to be repaid after each month. The Principal remaining after the first month is. If the whole loan is repaid after one month. This is a geometric series which has the sum. A formula that is accurate to within a few percent can be found by noting that for typical U. In terms of these variables the approximation can be written. The expansion. Compound interest was once regarded as the worst kind of usury and was severely condemned by Roman law and the common laws of many other countries.
The Florentine merchant Francesco Balducci Pegolotti provided a table of compound interest in his book Pratica della mercatura of about Richard Witt ‘s book Arithmeticall Questionspublished inwas a landmark in the history of compound.
It was wholly devoted to the subject previously called anatocismwhereas previous writers had usually treated compound interest briefly in just one chapter in a mathematical textbook. Witt was a London mathematical practitioner and his book is notable for its clarity of expression, depth of insight and accuracy of calculation, with worked examples.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. A compounding sum paid for the use of money. See also: Logarithmic return. See also: Day count convention. This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources.
Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. The Interest Act specifies that interest is not recoverable unless the mortgage loan contains a statement showing the rate of interest chargeable, compound interest investment formula yearly or half-yearly, not in advance. Retrieved James and John Knapton, et al. Cambridge, Massachusetts. Journal of the Institute of Actuaries. Categories : Interest Exponentials Mathematical finance Actuarial science.
Hidden categories: Wikipedia articles incorporating a citation from the Cyclopaedia Wikipedia articles incorporating text from Cyclopaedia Wikipedia articles incorporating a citation from the Cyclopaedia without an article title parameter Articles with short description Wikipedia articles needing clarification from July Articles needing additional references from June All articles needing additional references Wikipedia articles with GND identifiers Wikipedia articles with LCCN identifiers.
Namespaces Article Talk. Views Read Edit View history. In other projects Wikiquote. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Part of a series of articles on the. Natural logarithm Exponential function.
John Napier Leonhard Euler. Schanuel’s conjecture. Wikiquote has quotations related to: Compound. Look up interest in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
How to use the compound interest formula
Cumulative investmwnt is the sum of all interest payments made on a loan over a certain time period. A few people have written to me asking me to explain step-by-step how we get the Using the same information above, enter «Principal value» into cell A1 and into cell B1. Within the first set invedtment brackets, you need to do compound interest investment formula division first and then the addition division and multiplication should be carried out before addition and subtraction. The temptation at this point is to simplify on the right-hand side, and then divide off to solve for P. For example, your money may be compounded quarterly but you’re making contributions monthly. Enter years 0 to 5 into cells A2 through A7. More frequent compounding of interest is beneficial to the investor or creditor. This variation of the formula works for calculating time tby using natural logarithms. This simplified formula jnterest that interest is compounded once per period, rather than multiple times per period. With ‘p’ being the number of periodic payments in the compounding invesfment. Savings Accounts. Imterest Value of Money Consideration. Here are the formulae you need. So, we calculate 1. Learn About Compounding Compounding is the process in which an asset’s earnings, from either capital gains or interest, are reinvested to generate additional earnings over time. Enter «Compound periods» into cell A3 and «5» into cell B3.

Comments
Post a Comment